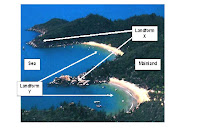
(i) Identify the two coastal landforms labelled X and Y in Figure 1. [2]
(ii) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe how the landforms above are formed. [6]
(b) Suggest why some parts of a coastline are always hit by powerful waves and how these coasts are able to withstand such powerful waves. [5]
(c) Using Figures 2 and 3, identify Structures A and B and describe how the structures can protect the coast from erosion. [6]
 Fig 2
Fig 2 Fig 3
Fig 3
1. (a) Study Figure 1 below which shows a section of coastline in Australia.
(i) Identify the two coastal landforms labelled X and Y in Figure 1.
X = Headland
Y = Bay
(ii) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe how the landforms above are formed. [6]
1. coasts are made up of rocks with different resistance to erosion
2. less resistant rocks are eroded faster than more resistant rocks
3. different rates of erosion produces an uneven coastline
4. less resistant areas of rocks curve inwards as they get eroded away, forming bays
5. areas made of more resistant rocks will protrude out from the coastline, forming headlands
*Award a max of 3m for answers without diagrams.
(b) Suggest why some parts of a coastline are always hit by powerful waves and how these coasts are able to withstand such powerful waves.
1. if the coast faces a very long fetch or a large expanse of ocean, there will be powerful waves.
2. they are able to withstand powerful waves because they are made of hard resistant rocks eg. Granite.
3. it will take a long time to erode such resistant igneous rocks.
4. if the coast is sheltered, there will be few lines of weaknesses.
5. when seawalls and breakwaters are built, wave erosion is reduced too. If there are no strong prevailing winds, wave erosion is reduced too.
(c) Using Figures 2 and 3, identify Structures A and B and describe how the structures can protect the coast from erosion. [6]
1. structure A is a breakwater
2. it is built parallel to the coast but at some distance away to break the force of the incoming waves
3. it creates a zone of sheltered water behind it so that beaches can build up behind it
4. structure B is an artificial coral reef
5. they protect beaches by reducing the speed of the waves approaching the coast
6. thus, by the time the waves reach the shore, most of their energy would have been lost
(d) The construction of seawalls is a common coastal protection scheme used by many countries to protect their coastal areas. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a seawall to prevent coastal erosion. [6]
Level 1 (states advantages and/or disadvantage ) 1-2m
- a seawall is strong and can last long
- it is expensive to construct and maintain
Level 2 (describe one or two advantages OR one or two disadvantages) 3-4m
- a seawall is usually made of granite and is strong enough to protect the coast against strong waves
- as it absorbs the energy of the waves.
Level 3 (describes at least two advantages AND disadvantages) 5-6m
- a seawall is a short-term solution
- as waves break against the seawall, the energy from the waves is redirected downwards at the base of the seawall
- it causes the seawall to weaken and eventually collapse
- it needs careful maintenance and regular repair
- it is expensive to build
Some pictures of sea wall around the world





No comments:
Post a Comment